This section describes the general series of steps used to install mod_perl and configure Apache to use it for executing fast CGI scripts. You should already have a current version of Perl and Apache up and running and have some familiarity with how CGI works (see Chapter 16).
The examples demonstrate how to install and run mod_perl scripts on a Windows system using Apache2.x and ActivePerl5.8.8.
For documentation, go to the mod_perl site, http://perl.apache.org/docs/index.html. To get source and binary mod_perl distributions, go to the download page at http://perl.apache.org/download/index.html. Configuring the Apache httpd.conf file may have some differences due to the fact that the Perl modules required are not necessarily located in the same library. It took some time to figure out how to adapt this to the current versions of Apache and Perl being used here.
There are two versions of mod_perl:
mp2—mod_perl for the 2.x.x branch of the Apache HTTPD Server.
mp1—mod_perl for the 1.3 branch of the Apache HTTPD Server.
For this example, we will be using mp2 is fully compatible with HTTPD 2.0.x, and supports most of the 2.2.x feature set.
Installation of modules has become increasingly simplified with ActiveState's PPM tool. It is included now with every ActivePerl release for not only Windows but also UNIX/Linux versons of ActivePerl. This tool allows you to install, remove, upgrade, and otherwise manage the use of common Perl pre-compiled CPAN modules.
The following examples use PPM on a Windows system.
|
Code View: C:\>ppm install mod_perl Downloading ActiveState Package Repository packlist...done Updating ActiveState Package Repository database...done ppm install failed: Can't find any package that provide mod_perl C:\>ppm install http://theoryx5.uwinnipeg /ppms/mod_perl-2.0.ppd Downloading mod_perl-2.0-2.0.3...done Unpacking mod_perl-2.0-2.0.3...done Generating HTML for mod_perl-2.0-2.0.3...done Updating files in site area...done Downloading mod_perl-2.0-2.0.3 install script...done Running mod_perl-2.0-2.0.3 install script... The Apache module mod_perl.so is needed to complete the installation, and should be placed in your Apache2 modules directory. I will now fetch and install this for you. Fetching http://theoryx5.uwinnipeg.ca/ppms/x86/mod_perl-2.0.so ... done! Where should mod_perl.so be placed? [C:/Apache2/modules] c:/wamp/Apache2/modu mod_perl.so has been successfully installed to c:/wamp/Apache2/modules done 465 files installed |
cd c:\wamp\Apache2\conf C:\wamp\Apache2\conf>dir /b alias httpd.conf httpd.default.conf magic magic.default mime.types mime.types.default |
The Apache httpd.conf file then must be modified by adding the following line:
#LoadModule mime_magic_module modules/mod_mime_magic.so
#LoadModule proxy_module modules/mod_proxy.so
#LoadModule proxy_connect_module modules/mod_proxy_connect.so
#LoadModule proxy_http_module modules/mod_proxy_http.so
#LoadModule proxy_ftp_module modules/mod_proxy_ftp.so
LoadModule negotiation_module modules/mod_negotiation.so
#LoadModule rewrite_module modules/mod_rewrite.so
LoadModule setenvif_module modules/mod_setenvif.so
#LoadModule speling_module modules/mod_speling.so
#LoadModule status_module modules/mod_status.so
#LoadModule unique_id_module modules/mod_unique_id.so
LoadModule userdir_module modules/mod_userdir.so
#LoadModule usertrack_module modules/mod_usertrack.so
#LoadModule vhost_alias_module modules/mod_vhost_alias.so
LoadModule php5_module "c:/wamp/php/php5apache2.dll"
LoadModule perl_module modules/mod_perl.so
#
# ExtendedStatus controls whether Apache will generate "full" status
# information (ExtendedStatus On) or just basic information (ExtendedStatus
# Off) when the "server-status" handler is called. The default
is Off.
===================================
|
We will now create the directory/folder where the mod_script programs will be stored. Instead of storing CGI scripts in this normal cgi-bin directory, they will be moved to this new directory, called c:/home/stas/modperl.
In this example, we will store Perl scripts in:
c:/home/stas/modperlDepending on your version of Perl, the Apache modules we will use to run existing Perl CGI scripts are located in the standard libraries found in the @INC array.
cd /c/ActivePerl/site/lib/ModPerl $ ls BuildMM.pm Manifest.pm RegistryLoader.pm BuildOptions.pm MapUtil.pm RegistryPrefork.pm CScan.pm MethodLookup.pm StructureMap.pm Code.pm ParseSource.pm TestReport.pm Config.pm PerlRun.pm TestRun.pm Const.pm PerlRunPrefork.pm TypeMap.pm FunctionMap.pm Registry.pm Util.pm Global.pm RegistryBB.pm WrapXS.pm MM.pm RegistryCooker.pm |
Next, we will create a file in Apache's conf directory for the most commonly used Perl modules. This file is called extras.pl and contains the modules that are most commonly used with mod_perl. By assigning this filename to the PerlRequire directive in the Apache configuration file, every time the Apache server starts, these modules will be loaded. (Note in most documentation for adding modules, the Registry.pm module is called Apache::Registry, but this module, under the current version of ActiveStatePerl, is now ModPerl::Registry.)
C:\wamp\Apache2\conf>more extras.pl use ModPerl::Util (); use Apache2::RequestRec (); use Apache2::RequestIO (); use Apache2::RequestUtil (); use Apache2::ServerRec (); use Apache2::ServerUtil (); use Apache2::Connection (); use Apache2::Log (); use Apache2::Const -compile => ':common'; use APR::Const -compile => ':common'; use APR::Table (); use Apache2::compat (); use ModPerl::Registry (); use CGI (); 1; |
Now we will edit the httpd.conf file, found under the Apache directory. For the version of Apache on this Windows system, the conf directory/folder is under the Apache2 folder.
Apache's conf Directory
C:\wamp\Apache2>dir /b
ABOUT_APACHE.txt
bin
cgi-bin
CHANGES.txt
conf
error
icons
include
INSTALL.txt
lib
LICENSE.txt
logs
modules
NOTICE.txt
README.txt |
Now we will cd into the conf directory and find the httpd.conf file.
Apache's Configuration file, http.conf
C:\wamp\Apache2>cd conf
C:\wamp\Apache2\conf>dir /b
alias
extra.pl
httpd.conf
httpd.default.conf
magic
magic.default
mime.types
mime.types.default |
Next, we edit the httpd.conf file by adding the lines in Example D.8 to the bottom of the file. (The numbers preceding each line are here only to explain each line in the Explanation section following the example.)
Editing Apche's Configuration File
Next, restart Apache.
There are a number of ways to check to see if mod_perl is actually working. You can look in the Apache error log after restarting the server, as shown here.
cd c:\wamp\logs C:\wamp\logs>dir /b access.log apache_error.log log_dir mysql_error.log php_error.log
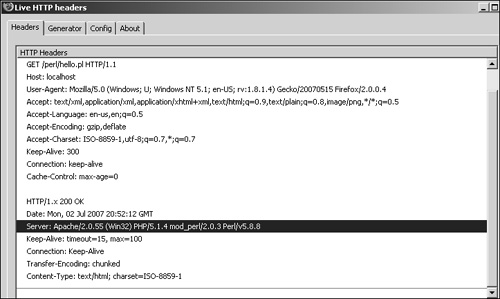
Check the Apache error log after restarting the server. You should see something like the following:
[Mon Jul 02 14:08:11 2007] [notice] Apache/2.0.55 (Win32) PHP/5.1.4 mod_perl/2. 0.3 Perl/v5.8.8 configured -- resuming normal operations [Mon Jul 02 14:08:11 2007] [notice] Server built: Oct 9 2005 19:16:56 [Mon Jul 02 14:08:11 2007] [notice] Parent: Created child process 5008
In the traditional cgi-bin directory under Apache's root directory, you will find a standard test file that is normally distributed with Apache. It is called printenv.pl. Copy this script to the new mod_perl directory you created, in this case c:/home/stas/modperl (see page 931), aliased as /perl/ in the http.conf file. Make sure permissions are set properly. This server should have execute permission for your script. If not, the following error will be sent to the browser (see Figure D.3).
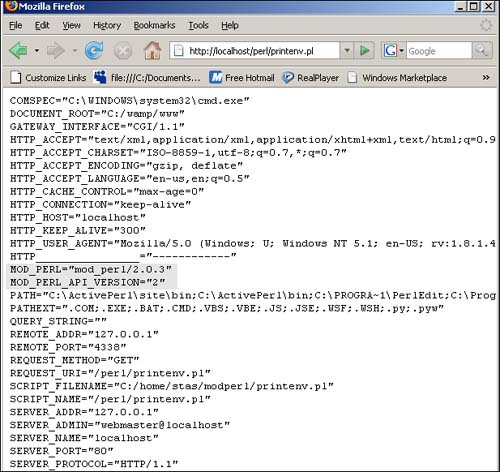
Now go to the URL in your browser and execute the printenv.pl file as shown in Figure D.4. This file displays environment variables, including the MOD_PERL and MOD_PERL_API_VERSION variables.
Try another CGI script:
Put the following CGI script in your mod_perl directory. This script uses CGI.pm, the object-oriented style. CGI Perl scripts should be executable from this directory once mod_perl is installed. (See: http://perl.apache.org/start/tips/registry.html.)
1 #!c:/ActivePerl/bin/perl.exe
2 use strict;
3 use CGI;
4 my $q = CGI->new;
print $q->header, $q->start_html(-title=>'First mod_perl Try',
-BGCOLOR=>'lightgreen'),
5 $q->h1('Hi, mod_perl is working!!'),
6 $q->end_html; |
The following script was copied and modified from:
Check for the version of Linux/UNIX you are using.
|
Code View: % cd /usr/src
%lwp-download http://www.apache.org/dist/httpd/binaries/httpd-2.0.55-sparc-sun-solaris2.8.tar.gz
% lwp-download http://perl.apache.org/dist/mod_perl-2.0-current.tar.gz
% tar -zvxf apache_1.3.20.tar.gz
% tar -zvxf mod_perl-1.26.tar.gz
% cd mod_perl-1.26
% perl Makefile.PL APACHE_SRC=../apache_1.3.20/src \
DO_HTTPD=1 USE_APACI=1 EVERYTHING=1
% make && make test && make install
% cd ../apache_2.0.55 (Check for the correct number here)
% make install
|
The mod_perl project features a lot of documentation, for both mod_perl 1.0 and 2.0. If there is anything you need to learn about mod_perl, you'll learn it here.
We use a number of conventions in this documentation, that are mostly easy to understand; if you're in doubt, look here for the explanation.
A collection of the documents specific to the mod_perl 1.0 generation.
A collection of the documents specific to the mod_perl 2.0 generation.
Here you can find documentation concerning mod_perl in general, but also not strictly mod_perl related information that is still very useful for working with mod_perl. Most of the information here applies to mod_perl 1.0 and 2.0.
mod_perl books, articles, presentations, and links to sites covering other relevant topics.